#3. Electrostatic Potential Due To An Electric Dipole

We already know that electric dipole is an arrangement which consists of two equal and opposite charges +q and -q separated by a small distance 2a. Electric dipole moment is represented by a vector p of magnitude 2qa and this vector points in direction from -q to +q. To find electric potential at point P due to a dipole consider charge -q and charge +q separated by a distance 2a. r1 and r2 respectively are distance of charge +q and -q from point P.
Since electric potential obeys superposition principle so the net potential due to electric dipole as a whole would be sum of potential due to both the charges +q and -q. Thus
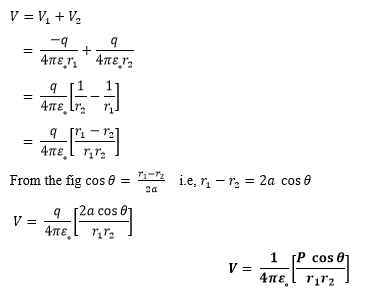
Special Cases
Potential at a point on the axial line i.e θ = 0

Potential at a point on the equatorial line i.e θ = 0
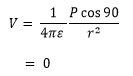
You may interested in Previous Year Question Paper With Answer Key
Browse more topics under Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance
- Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy, Potential Energy Difference
- Potential Due To A Point Charge
- Potential Due To An Electric Dipole
- Equipotential Surface & Its Properties
- Potential Energy In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To A Single Charge In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To A System Of 2 Charges In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To An Electric Dipole In An External Electric Field
- Electrostatics Of The Conductor
- Dielectric And Polarization
- Capacitor And Capacitance
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Effect Of Dielectric On A Capacitor
- Energy Stored In A Capacitor
- Van De Graaff Generator
Comments
Post a Comment