#8. Dielectric And Polarization
What are dielectrics?
Dielectrics are non-conducting substances or insulators. Dielectrics can be easily polarized when an electric field is applied to it. Thus their behavior in an electric field is entirely different from that of conductors.

Electric Field Inside A Dielectric
Consider a plate of conductor a positively charged one & another plate of a conductor which is negatively charged. So, in between them there exist electric field Eout from positive plate to negative plate. Now we are going to place a dielectric inside this electric field. under the influence of this electric field, the dielectric get polarised (polarisation means giving direction). Inside the dielectric there exist positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. The positively charged protons will move towards the negative plate and negatively charged electrons move towards the positive plate. As the result of this alignment of charges, an internal electric field Ein get produced, whose direction is opposite to Eout and the magnitude is less than Eout
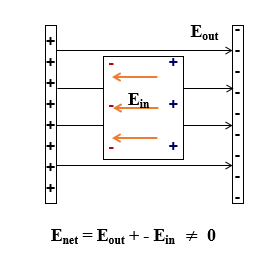
The electric field inside the dielectric Ein, only weakened the external electric field Eout. Not completely canceled. This is due to the fact that inside the dielectric, the number of free charge carriers are less than the conductor.
Classification Of Dielectrics
Depends upon the atomic structure, the dielectrics can be classified into 2 types

Non-Polar Molecule
A non-polar molecule is the one whose 'center of gravity' of positive charges(protons) and the center of gravity of negative charges(electron) coincide. Thus, this molecule doesn't have a permanent dipole moment.
Example for non polar molecules are Hydrogen H2, Oxygen O2, Nitrogen N2 etc
Polar Molecules
A polar molecule is the one whose 'center of gravity' of positive charge (protons) and the the center of gravity of negative charges(electron) does not coincide. Thus, this molecule has a permanent dipole moment. But the electric dipole moment of these polar molecules are in random direction and they all cancel each other. So, we can say in the absence of electric field the net dipole moment is zero in the case of polar molecules
Example for non polar molecules are HCl, H2O, NH3 etc
Now let see what happen when these polar, non-polar dielectrics placed in an electric field
When Non-Polar Dielectric Placed In An Electric Field
A dielectric may be made up of polar or non-polar molecules, the effect of electric field is almost same.
Let us consider a non-polar dielectric placed in an external electric field. The positive center move towards the negative plate(negative side of EF) and the negative center move towards the positive plate(positive side of EF). That is the positive center and negative center get displaced in opposite direction.

Now the molecules develop an induced dipole moment and we can say the dipole gets polarized. The induced dipole moments of different molecules add up to give the net dipole moment of the non-polar dielectric.
When Polar Dielectric Placed In An Electric Field
In the case of polar dielectric, each molecule has permanent dipole moment but, in the absence of electric field the electric dipole moment of these polar molecules are in random direction and they all cancel each other. Now let see what happen when a polar dielectric placed in an external electric field

In the presence of an external electric field, the positive center move in the direction of the electric field and the negative center move in the opposite direction. In other words, the molecules tend to align themself with the direction of the field. And now the dielectric is polarized.
You may Interested In Physics Previous Question Papers With Answers
Browse more topics under Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance
- Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy, Potential Energy Difference
- Potential Due To A Point Charge
- Potential Due To An Electric Dipole
- Equipotential Surface & Its Properties
- Potential Energy In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To A Single Charge In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To A System Of 2 Charges In An External Electric Field
- Potential Energy Due To An Electric Dipole In An External Electric Field
- Electrostatics Of The Conductor
- Dielectric And Polarization
- Capacitor And Capacitance
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Effect Of Dielectric On A Capacitor
- Energy Stored In A Capacitor
- Van De Graaff Generator
Comments
Post a Comment